High demands on current methods of non-destructive testing (NDT) also include requirements for analysis of the internal structure of materials and verification of the properties of the given material (porosity, content of material in the sample, defects, etc.). It is also often necessary to scan optically inaccessible geometry and shape. X-ray computed tomography is a progressive method that is used today for exactly these purposes.


The first field where computed tomography (CT - computed tomography) was applied in the first half of the 70s was medicine. Here it has proven itself as a unique diagnostic tool. Only twenty years later, with the development of technology, this method was also extended to the field of industry. Here, since then, it has been used mainly for the inspection of industrial workpieces, for the analysis of voids and material defects. Technological developments within a few years have moved this method among the key tools of NDT.

Radiography enables 2D transmission imaging of an object using X-ray radiation. Based on the different ability of different materials to absorb X-ray radiation, we get their shadow image. This simple method enables real-time control of assemblies, search for mechanical defects, food inspection, etc.
If we use the principle of digital radiography and obtain a set of projections of the object in 360 degree rotation, we can put the individual images back into a three-dimensional voxel model (a voxel is a volumetric equivalent of a pixel). This model will contain comprehensive information about the internal and external geometry of the object, including optically inaccessible areas, defects and material defects. We can then analyze this data with powerful software tools and visualize the results as desired. Sometimes this technology is referred to as 3D CT scanning.
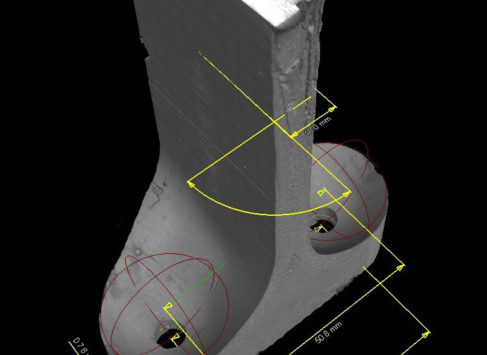
Determination of external and internal geometry with high accuracy from one scan (2D/3D dimensioning).

Evaluation of material wall thickness and gap width using a histogram.
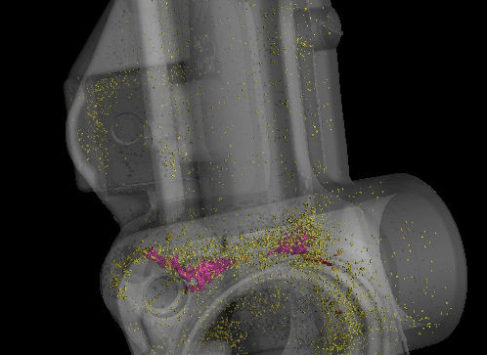
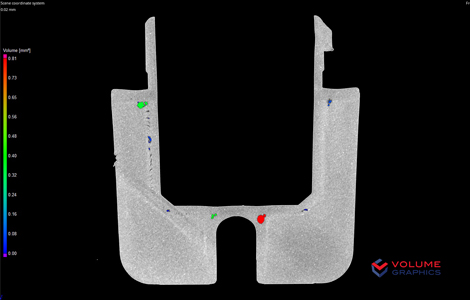
Comprehensive analysis of inclusions, pores and other defects inside the material.
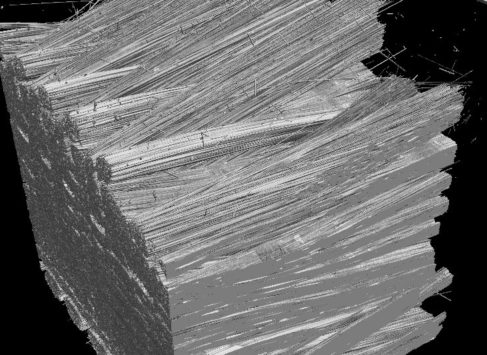
Analysis of fiber orientation in composite materials.
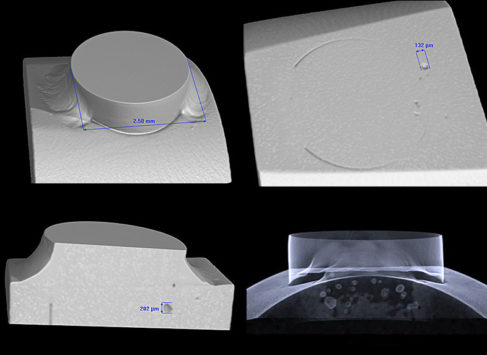
Laminographic inspection of joints, welds and joints.
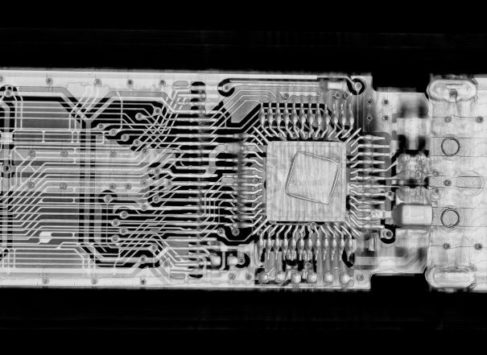
Fine structure inspection of additive manufacturing and electronics (SMD).
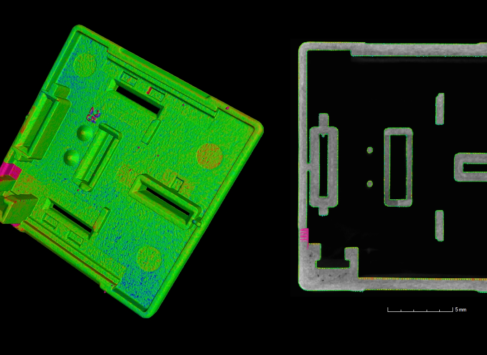
A quick method to compare a CAD model against a scan or two scans against each other.
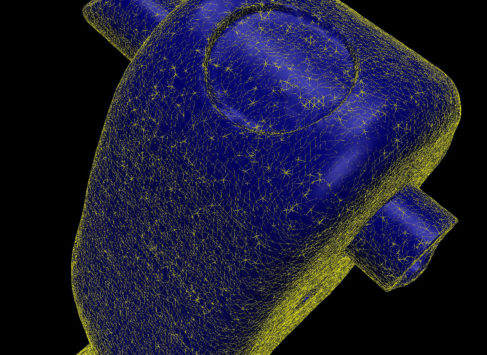
Creating a CAD model based on a polygon network obtained by 3D CT scanning.

serves for non-destructive inspection of mechanical arrangement or material defects in 2D view
in real time.